If you feel your anxiety levels rising every time you open a news app, watch the headlines on TV, or get a glimpse of social media, you’re not alone.
Not only are the scenes of devastation caused by the Russian invasion of Ukraine shocking and upsetting, but the implications of the conflict for the rest of the world are hard to ignore – especially at a time when it seemed like the pandemic was finally waning.
“We are now faced with another massive world event that is out of our control, and could impact our lives substantially,” says Dr. Elena Touroni, consultant psychologist and co-founder of The Chelsea Psychology Clinic – and this can “make us feel very anxious”.
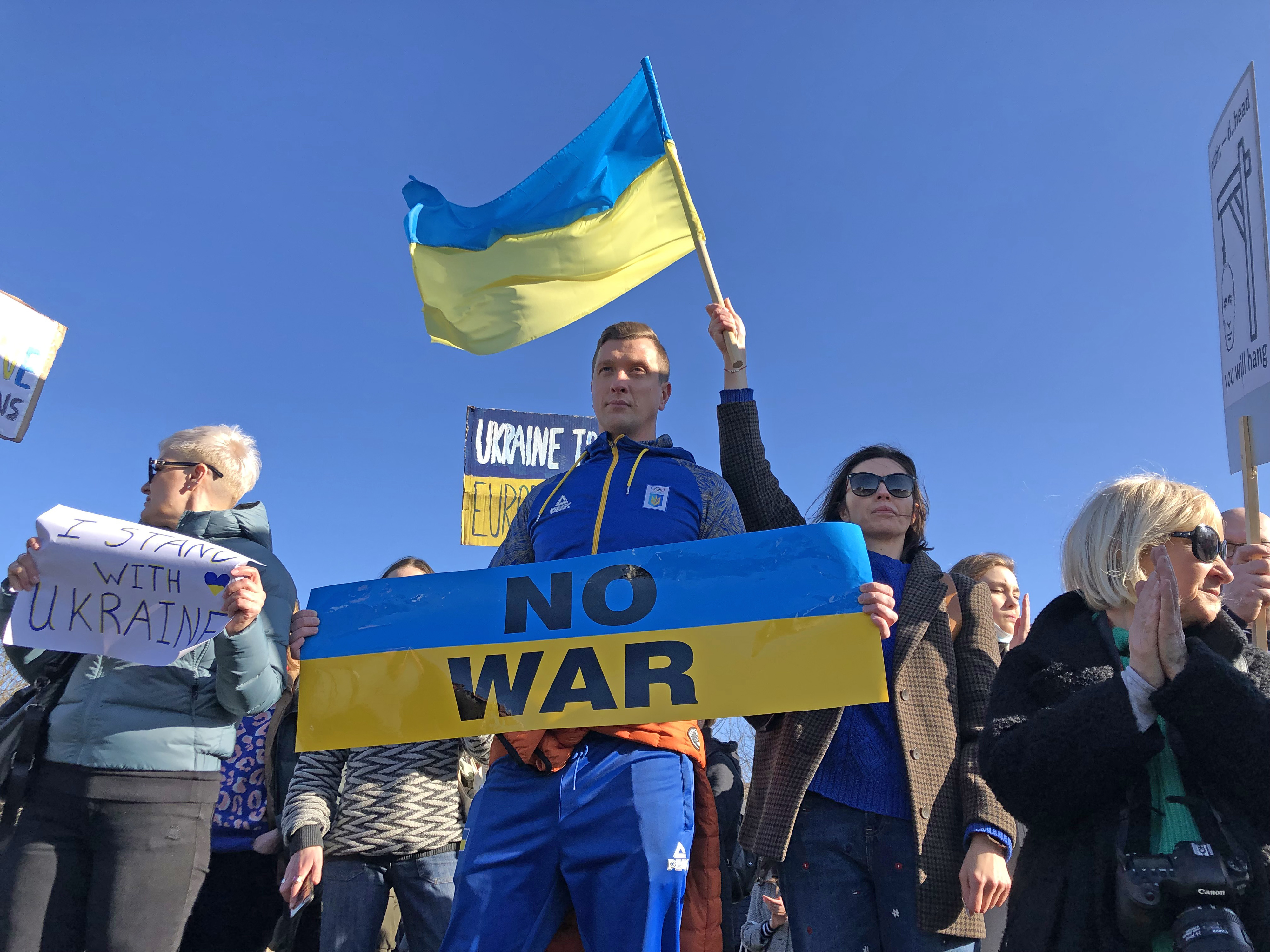

While there are some steps you can take to support the Ukrainian people – such as donating to relevant charities or joining protests – it’s important to look after your own mental health if reading the news has become a source of stress.
“It’s no surprise that lots of us are either gripped by what’s in the news or choose to avoid it entirely,” says Madeleine Gauffin, licensed psychologist and psychotherapist at the digital healthcare provider, Livi. “We have to find a way to process what’s going on, and use tools to manage feelings of fear and anxiety.”
We ask experts for their advice on how to cope when your thoughts start to spiral…
Limit news consumption
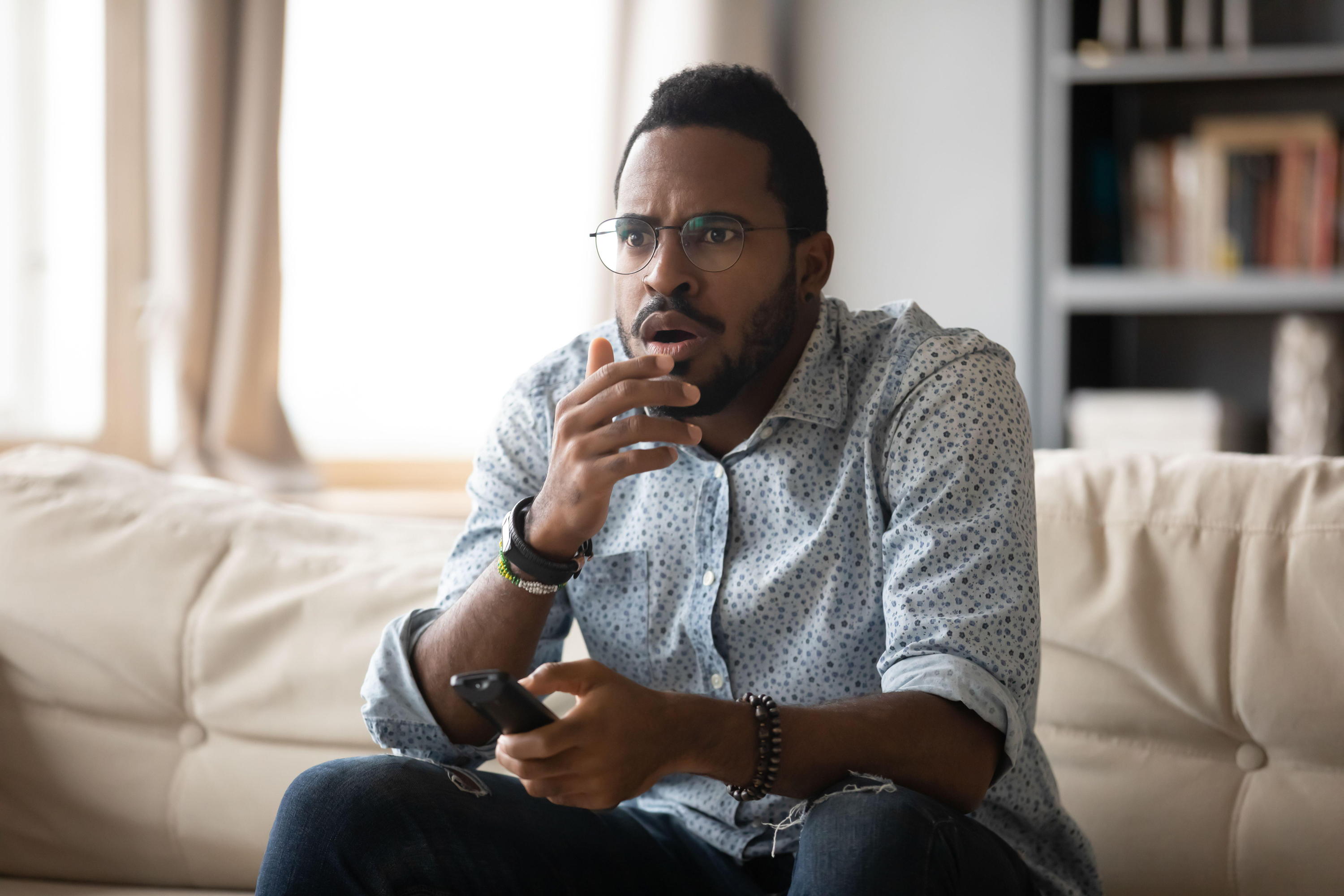

You may feel a compulsive need – or even a responsibility – to keep abreast of developments, especially if current affairs are a topic of conversation amongst friends or colleagues, but ‘doomscrolling’ (endlessly checking for updates) can be hugely detrimental.
“It’s important to restrict your screen time, especially if you’re prone to anxiety, as you’ll probably find social media and the news especially triggering,” says Touroni. “Obviously you’ll want to remain up to date, so set yourself a limit to how often you check – for example, twice a day.”
But what if you feel guilt that you’re burying your head in the sand while people are suffering terrible hardships?
“We should always recognise our own limitations,” says certified coach Phil Drinkwater. “It’s incredibly sad that some people don’t get to choose to ignore what’s happening, but overwhelming ourselves won’t solve their issues.”
Allocate time for worrying
This may sound counterintuitive, but giving yourself permission to focus on your fears can help – by getting them ‘out of your system’.
“Allow yourself ‘worry time’ when you’re in a safe place,” says Lyni Sargent, trainee art psychotherapist and founder of Starleng (hello05236.wixsite.com/starleng).
“Give yourself 10 minutes to worry about whatever worries pop up, and write them down. It’s doesn’t have to be an essay, just quick bullet points.”
Challenge negative thoughts
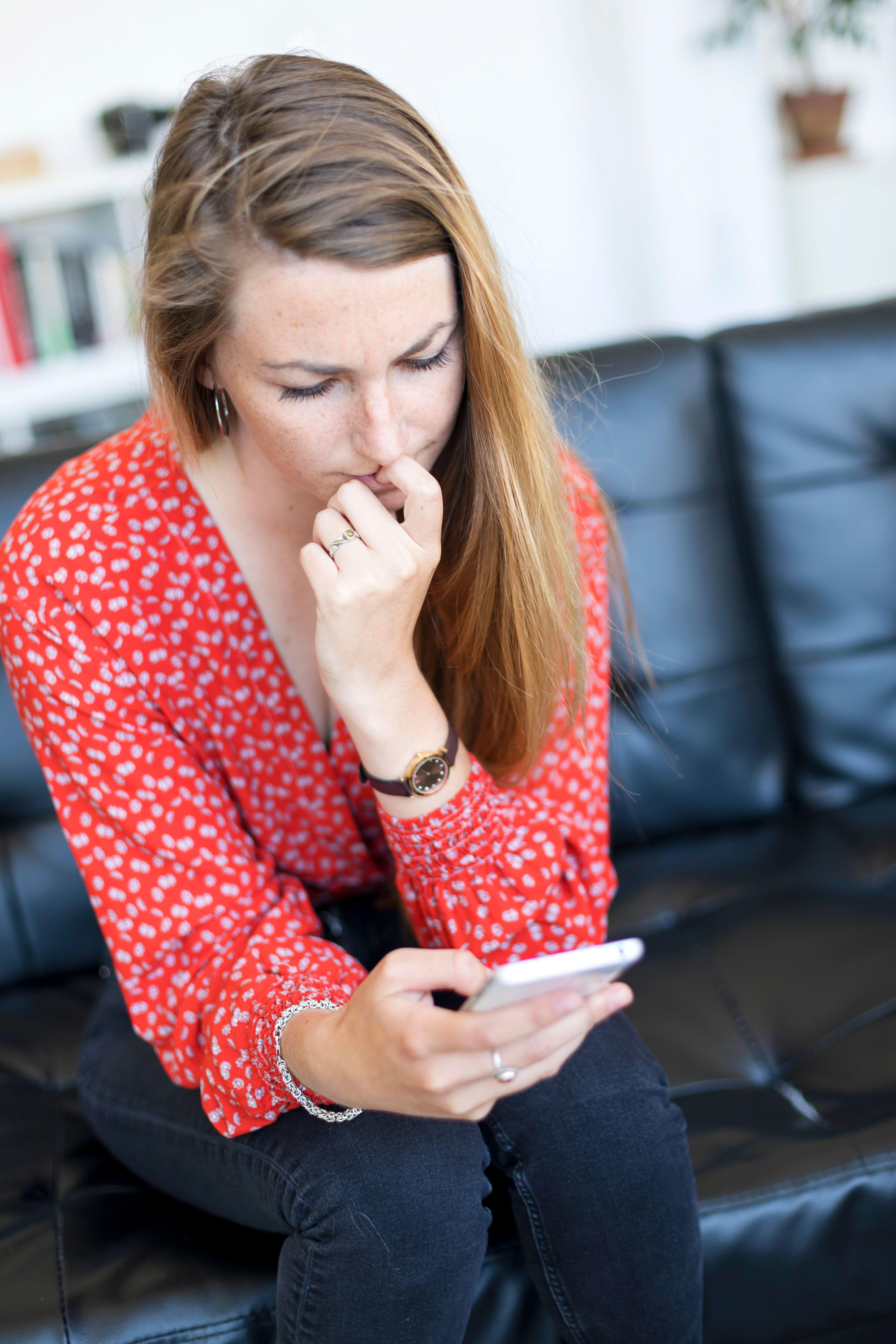

“During times like this, it can be easy to spiral into catastrophic thinking,” says Touroni. For example, in this instance it might be thinking one conflict will lead to widespread war.
“When you notice that you’re having a catastrophic thought, tell yourself it’s just that – a thought – and it’s not necessarily representative of reality. Take it one day at a time, and don’t try to predict the future, or consider the most negative outcome.”
Drinkwater says: “Anxiety can be calmed by recognising the future – particularly a future involving the decisions of hundreds of people – is too difficult for us to correctly predict.”
He suggests gently pushing back against these anxious thoughts. “Follow this process in your mind: ‘Oh! I’ve just had a thought! Thank you for that.
I recognise you’re trying to protect me. Do you have any clear evidence of the certainty of this outcome? How likely is this to happen? Not very likely? OK, well thank you for the opinion, but I’ll deal with this situation if – and only if – it happens’.”
Ask for help if you need it
For some people, self-soothing with these types of coping strategies is very effective, or maybe it has been in the past – but sometimes you may need some additional support.
Sargent advises: “If you find these things are no longer providing a sense of relief, and if you find that you can’t control the negative thoughts – if they are disturbing your everyday activities or disrupting your sleep – then it’s important to speak to your GP.”