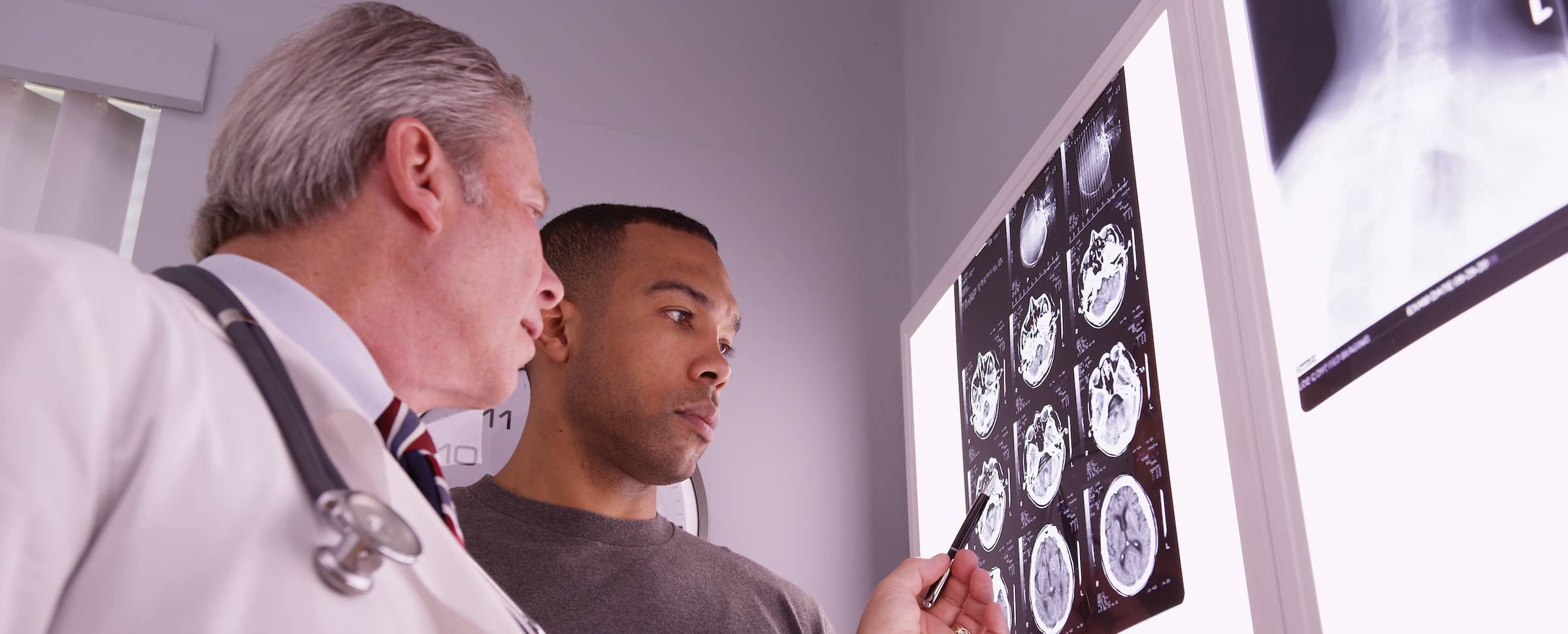
Head injuries and the problems they cause have been highlighted recently after a ban came into force preventing Scottish footballers from heading the ball before and after matches.
This has been a problem for a while as repeatedly coming into contact with a ball at speed can be traumatising for the brain and head. This ban is a positive move to help protect players from harming themselves and causing lasting damage.
Any type of head injury can have a lasting impact on those who have been affected. It can also affect their loved ones as they try to understand the changes that have taken place.
You’re not alone if someone you love has experienced a head injury, as according to Headway, the brain injury association, 356,699 UK admissions to hospitals in 2019-20 were for those with acquired brain injury.
This guide takes you through the ways that a brain injury can impact everyday life and the signs that you can look out for.
Types of brain injury
There are different types of brain injury and it’s worth having an idea of what these are so that you know what type is affecting your loved one. There are traumatic and non-traumatic brain injuries:
Traumatic
- Traumatic injuries are caused by an external force affecting brain function. These include concussion, which is where the brain functions differently after hitting the internal walls of the skull – this is the most common traumatic brain injury.
- Hematoma is usually caused by a ruptured blood vessel, edema is the swelling of the brain and can be caused by any type of brain injury, and a diffuse axonal injury makes the axons of the brain cells unable to function. Skull fractures are rare, but they can change brain function and in some cases, infections can occur.
Non-traumatic
- Non-traumatic brain injuries are caused by internal problems, such as pressure caused by a tumour or a loss of oxygen. Haemorrhages, strokes, and hypoxic/ anoxic – where there’s a shortage of oxygen – are all types of non-traumatic brain injury.
Effects of a brain injury
The effects can be very similar, whether it’s a traumatic or non-traumatic injury to the brain. Here are some of the ways that people can be impacted:
Cognitive
It can be common for those affected by brain trauma to have issues with their memory. They can become forgetful and struggle to recall basic facts. Similarly, they can have a shorter attention span and processing information can become particularly difficult.
Behavioural
You might notice your loved one behaving differently. For example, it can be common for those with a brain injury to say things that are out of character or act impulsively. This is because of the change in the way the brain is functioning.
Emotional
It affects them on an emotional level too. Understandably, they’re likely to feel upset about what happened to them. After all, a change in the way your brain operates can be life-changing.
Low moods, anxiety, stress and depression are all potential emotional and mental effects of a brain injury.
How to help
Knowing what to look out for is the first step towards helping your loved one. Understanding that there will be a change in how they behave is key to being there for them. If you need more help, organisations like Headway offer support.
Additionally, you may need financial support – especially if you have to change your home setup or they can no longer work due to their injury.
If the injury was the result of an accident and it wasn’t their fault, you may want to consider seeking compensation. Speaking to specialist brain injury solicitors could give you an idea of the type of damages that your loved one could receive.
Being there for them is important. It can be tough, but with the right support, you can support them through the days and weeks after their injury and beyond.