Dame Deborah James has died at the age of 40, her family have announced.
The much-loved presenter of the BBC podcast You, Me And The Big C, and mum-of-two, raised millions of pounds for research through the Bowelbabe Fund before she died – and leaves behind an important legacy.
Her family posted on Instagram: “Deborah shared her experience with the world to raise awareness, break down barriers, challenge taboos and change the conversation around cancer. Even in her most challenging moments, her determination to raise money and awareness was inspiring.
“A few final things from Deborah… ‘find a life worth enjoying; take risks; love deeply; have no regrets; and always, always have rebellious hope. And finally, check your poo – it could just save your life’.”
Throughout her journey, James shared candid Instagram posts on her progress and videos showing her dancing her way through treatment – her positivity was truly inspirational.
So, from the symptoms James wanted everyone to check to the treatments available, here’s what we should all understand about bowel cancer…
How common is bowel cancer?
Dr Lisa Wilde, director of research and external affairs at Bowel Cancer UK, says: “Bowel cancer is the fourth most common cancer in the UK and the second biggest cancer killer, affecting both men and women.
Every 15 minutes someone is diagnosed with bowel cancer, which is nearly 43,000 people every year.”
What are the main symptoms?
“Persistent and unexplained changes in your bowel habits – you may notice that you need to poo more frequently and your stools are looser,” says Dr Nikki Ramskill, GP at the digital healthcare provider, Livi. What’s normal for you might be abnormal for someone else.
Noticing blood in your poo or coming from your bottom is another sign, “Often it is dark red or brown in colour,” she says.
While “unexplained weight loss; extreme tiredness for no obvious reason; a pain or lump in your tummy” are other warning signs adds Wilde.

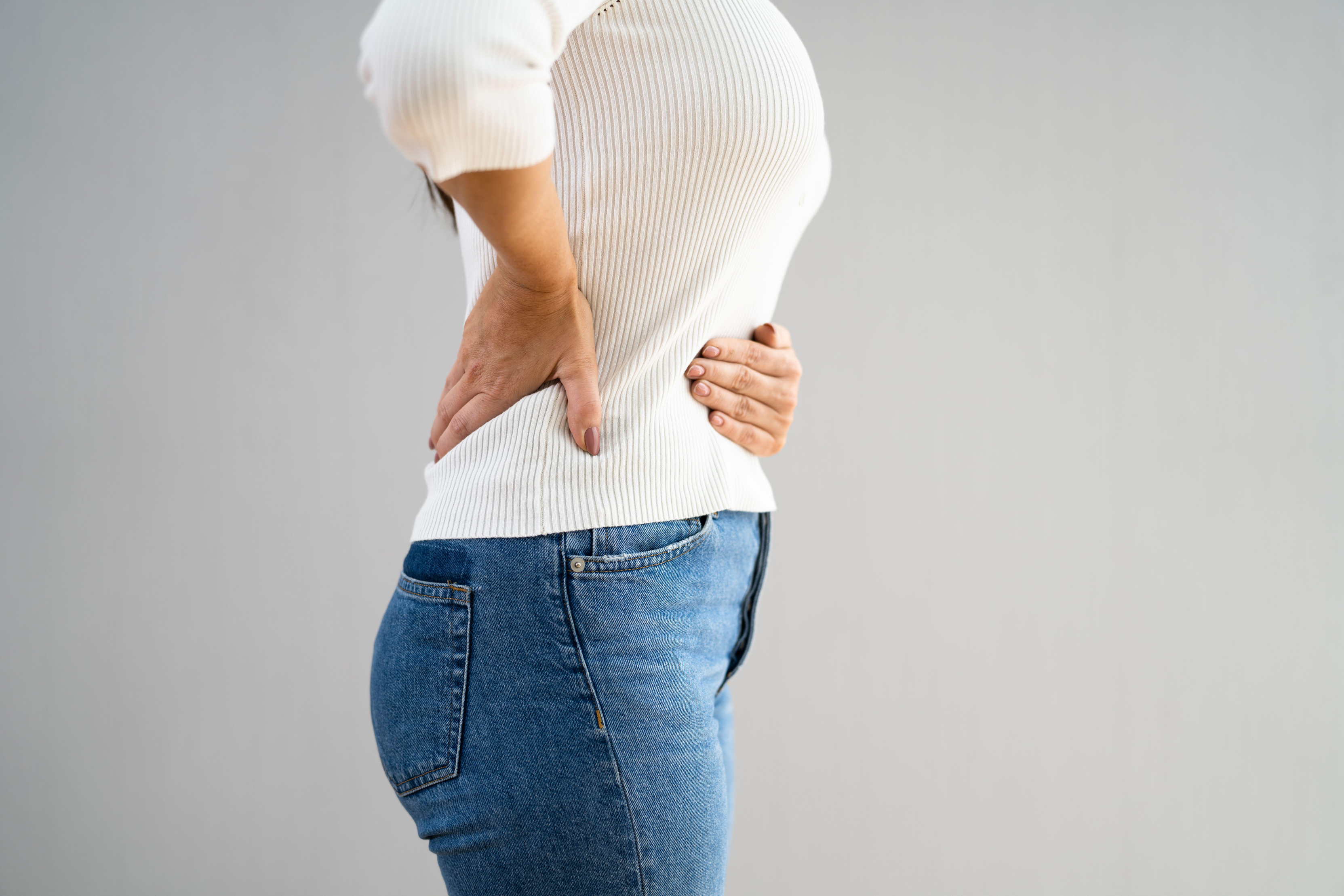
In some cases, bowel cancer can stop digestive waste from passing through the bowel. “This is a medical emergency and you should seek urgent medical care,” warns Ramskill.
Signs of this happening include sickness with constant swelling around your abdomen and abdominal pain brought on by eating.
Could the symptoms mean something else?
Quite possibly, but it’s so important to find out what’s causing any of these signs.
“Having these symptoms does not always mean you have bowel cancer – they can often be a sign of other common conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), an infection, or inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis,” says Ramskill.
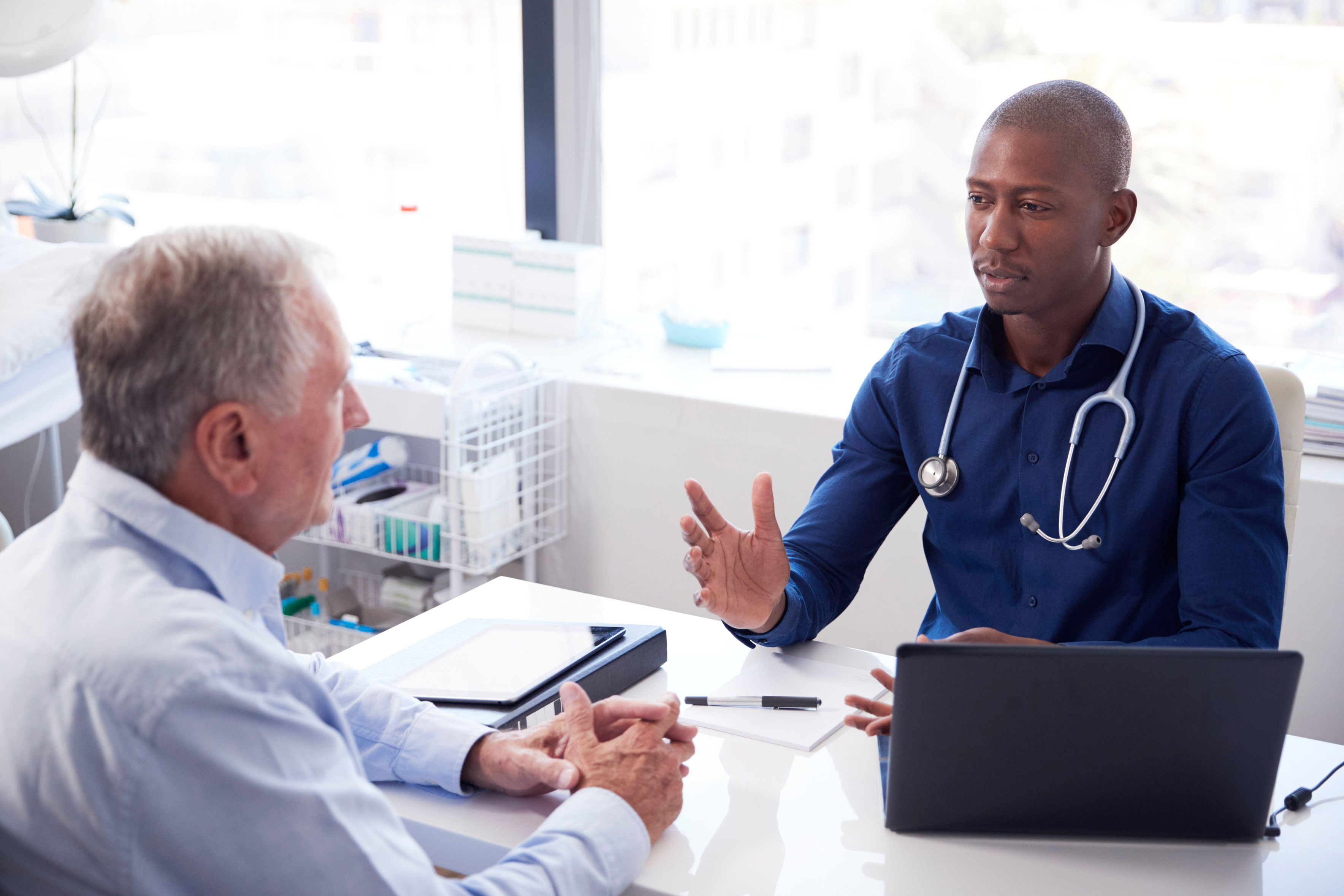
What will happen at the GP appointment?
It’s a good idea to keep a symptoms diary ahead of your appointment to discuss with the doctor. “On the day, your doctor may want to examine your tummy and bottom to check for any lumps.
You may also be asked to take a blood test – this will check for an iron deficiency which can be a sign of bowel cancer,” says Ramskill.
“In some cases, you may also be required to provide a stool sample, this is so that your poo can be checked for blood – another symptom of bowel cancer.”

How treatable is it?
“Bowel cancer is treatable and curable especially if diagnosed early,” says Wilde. “Nearly everyone survives bowel cancer if diagnosed at the earliest stage, but this drops significantly as the disease develops. Early diagnosis really does save lives.
“Being aware of the symptoms and visiting your GP if you are concerned can help increase chances of an early diagnosis.”
What’s a FIT test?
Your GP might request you do a FIT (Faecal Immunochemical Test) which helps to detect bowel cancer at an early stage, when treatment has the best chance of working, explains Wilde. It can be carried out at home.
“The test can also find polyps (non-cancerous growths), which might develop into cancer. Polyps can usually be removed, to lower the risk of bowel cancer.
“The FIT test looks for hidden blood in poo and you can take the test in the privacy of your own home. The test has a stick attached to the lid, which is used to take one small poo sample and placed back into the tube.
It’s then sent to a screening centre and you will be notified of your results in about two weeks,” she says.
What’s a colonoscopy?
Your doctor may also refer you for a colonoscopy at the hospital if they suspect something isn’t quite right about your bowel or colon. It’s a very common procedure – thousands are carried out across the country every week.
“The procedure involves an endoscopist putting a thin flexible tube with a camera on the end up your bottom so they can see the inside of your bowel,” says Wilde.
“[It] gives a close-up view of the inside of your bowel so they can clearly see if there’s anything wrong. A colonoscopy can feel a little uncomfortable, but it’s an important part of maintaining good all-around health.
Most people who have a colonoscopy won’t have bowel cancer. But, if bowel cancer is detected at its earliest stage, nearly everybody is treated successfully.”
What treatment is available?
“If you are diagnosed with bowel cancer, you will be cared for by a multidisciplinary team who will discuss your treatment options depending on which part of your bowel is affected, how far the cancer has spread and your general health,” says Ramskill.
“This can include surgery combined with chemotherapy, radiotherapy or biological treatments.”In some cases a colostomy or ileostomy (stoma) may be needed.
Donate to Deborah James’ fund at bowelbabe.org.